Table of Contents
Accurate thread testing is becoming increasingly important in series production.
Thread testing
Our thread testing technology is built upon the MultiPro 3G control system and is specifically designed for automated testing of both internal and external threads using thread gauges when paired with our dedicated thread testing nutrunner.
In view of the increasing importance of precise thread testing in modern series production processes, we have developed this technology.
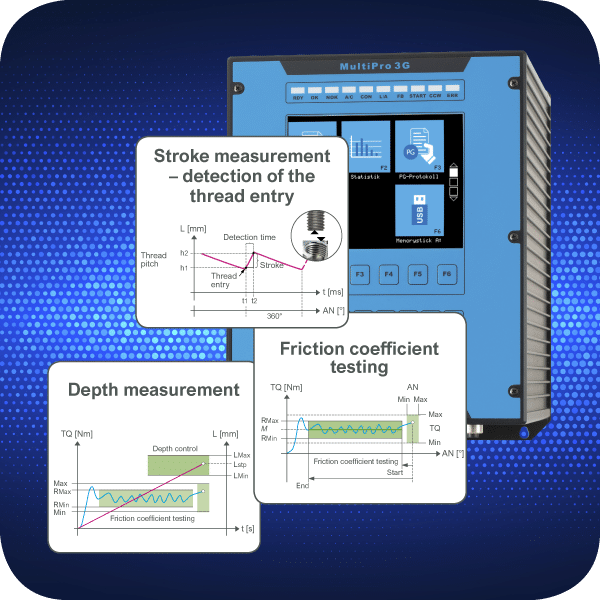
A new dimension in thread testing is opened up by using the DSM test nutrunner with changeable thread gauges in combination with intelligent measurement technique. This not only enables automated and stable testing procedures but also comprehensive documentation of the entire process.
Thanks to the modularity of our nutrunner and control system, the equipment can be flexibly adapted to individual requirements. Whether it’s the nutrunner itself, the low-backlash output adapted to it, an attachable position sensor, or the execution of the thread gauge – our inspection system enables the efficient testing of all threads in your production.
By the way:
The optional monitoring function can also be used in conventional tightening processes, where it is possible to measure and analyse the screw depth in addition to the torque and angle of rotation and use it as a preset parameter.
The benefits of our thread testing solution
- Compact design, based on standard tightening system.
- Flexible test strategy with up to 99 possible test steps.
- Gentle screw-on pressure thanks to spring elements (optional adjustable).
- Storage of up to 128 different test programmes.
- Optional: Special test gauge holder to compensate small alignment errors by decoupling the gauge from the axis of rotation.
- Optional: The automatic changeover unit allows for the automatic switching of the inspection gauge or, in case of a malfunction, its disconnection.
Data sheet
Here you will find the corresponding technical data sheet for our Threat test nutnunner with a example sequence. You can view or download the document directly in the browser.
Meaning (Videoclip)
In the following german explanatory video you will learn why thread testing is so important in the industrial assembly of assemblies and what solutions DSM offers for this.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationCalibration
Did you know that you can have your devices calibrated directly in-house?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is automatic thread testing?
Automatic thread testing is a computer-controlled process that inspects threads for dimensional accuracy, pitch, depth, and defects using sensors, cameras, or motorized gauges. It ensures consistent quality in threaded components without manual intervention.
2. What are the benefits of automatic thread testing compared to manual inspection?
Automated systems offer faster inspection speeds, higher repeatability, reduced human error, and comprehensive data logging for quality assurance. They enable 100% inspection in high-volume production environments.
3. Which thread features can be checked automatically?
Key features include pitch, flank angle, major and minor diameters, thread depth, concentricity, and the presence of burrs or contamination. Advanced systems can also detect incomplete or damaged threads.
4. How does an automatic thread testing system work?
The system uses mechanical or optical sensors to scan the thread geometry and compares the measurements to predefined tolerances. Results are processed in real-time, often with integrated feedback to the production line.
5. In which industries is automatic thread testing commonly used?
It is widely used in automotive, aerospace, mechanical engineering, and medical device manufacturing—anywhere high-precision threaded components are critical.
6. Can automatic thread testing systems be integrated into existing production lines?
Yes, many systems are modular and can be integrated inline or offline, with interfaces for MES or ERP systems to support traceability and process control.
7. What technologies are used in automatic thread testing?
Technologies include motorized torque sensors, optical inspection with cameras, laser measurement systems, and force-displacement sensors for functional testing.
8. How does automatic thread testing contribute to quality assurance?
It enables early detection of defects, ensures compliance with specifications, reduces rework and scrap, and provides documentation for audits and certifications.
Note: This FAQ is intended for general informational purposes and does not replace personalized advice. For specific inquiries, please consult a qualified specialist.