Press-in technique
Servo-Electric Press-In Technology for Perfect Connections
Press-in Technique
Press-In Technology by DSM
DSM offers servo-electric press-in units for a wide range of applications — from sensitive processes starting at 50 N up to powerful press-in operations with forces up to 120,000 N. Depending on the requirement, the units are equipped with extended stroke, electromechanical brake, or backstop.
Thanks to in-house development and manufacturing, individual adaptations are always possible — both mechanically and in terms of control technology.
Stroke measurement can be performed either relatively or absolutely, with the appropriate measurement method flexibly defined via the control system.
DSM provides three series in the field of press-in technology, each with graduated performance levels and functionality:
Click the respective button to download the form directly. Complete the inquiry form, save it, and send it via email to DSM or upload the saved file through the contact form.
Joining — A Simplified Definition
According to DIN ISO 857–1 joining is defined as follows:
Joining refers to the process of connecting or combining two or more separate components to create a unified structure or system.
During this process cohesion is created locally and increased as a whole.
Simply put joining is the permanent connection of two or more workpieces with each other through screws, rivets or bolts.
Joining technology also includes fusion with the help of shapeless materials, for example by using an adhesive.
This results in a connection between workpieces that can be both rigid and movable.
Joining Methods
The DIN 8593 standard includes a categorization of joining and joining technology, respectively into various methods.
These are:
- Putting together
- Filling
- Pressing on/in
- Shapeless forming
- Forming
- Welding
- Soldering
- Bonding
- Textile joining
The following table provides an overview of the individual joining methods and their application fields:
| Joining Method | Definition | Field of Application |
|---|---|---|
| Putting together | Joining, placing, setting, inserting, fitting together, hanging, hooking, aligning, partial spreading of two workpieces. | Assembly |
| Filling | Filling of voids or containers with shapeless materials. | Impregnation |
| Pressing on/in | Elastic deformation of workpieces through screws, clamps, clips, press connections, nailing, wedging, tensioning. | Electrical engineering, mechanical engineering |
| Shapeless forming | Connecting workpieces with an additional workpiece or shapeless material. | 3D-printing |
| Forming | Shaping workpieces through bending, flanging, necking, narrowing, folding, notching, grooving, riveting, spreading, overlapping, widening. | Automotive industry, household appliances industry |
| Welding | Joining workpieces through heat/force with/without filler metal (shielding gas, welding powder, fluxes, pastes) | Automotive industry, mechanical engineering, steel and metal construction |
| Soldering | Creating a surface to alloy through heat. The workpiece itself is not deformed. | Electrical engineering |
| Bonding | Inseparable and material-bonded connection of workpieces through adhesives. | Automotive industry, aerospace |
| Textile joining | Connecting workpieces through form fit, force fit or material fit. | Textile manufacturing |
All press-in units by DSM are designed for the press-in methods of pressing on/in as well as forming.
Application field
Precision press-in, press-in to a stop, riveting, bending, embossing/forming, testing/measuring, caulking, clipping, checking switch/latch points and calibrating.
The DSM press-in technology series covers the following compressive and tensile forces:
- XMP-Series: 0.5 kN bis 100 kN
- QMP-Series: 2.5 kN bis 120 kN
- SMP-Series: 0.25 kN bis 70 kN (only compressive forces)
The XMP Series
The DSM XMP Series characterized above all by its modular design, which ensures exceptional flexibility.
The integrated gearbox module, a variable high-precision force transducer, an absolute stroke measuring system, a large light field, and the MultiPro 3G control system together provide a flexible solution for both simple and complex assembly tasks. In combination with the MultiPro 3G, the system also enables high assembly accuracy and complete documentation of production data.
A brushless, electronically controlled servo motor drives the XMP press-in unit. Thanks to the modular design, additional options such as a motor holding brake (MB), a backstop (RS), and a holding brake (HB) can also be integrated.
Forces
The XMP press-in technology is designed for compressive forces as well as combined compressive and tensile forces. The integrated force sensor is available in various measurement ranges and can optionally be configured redundantly.
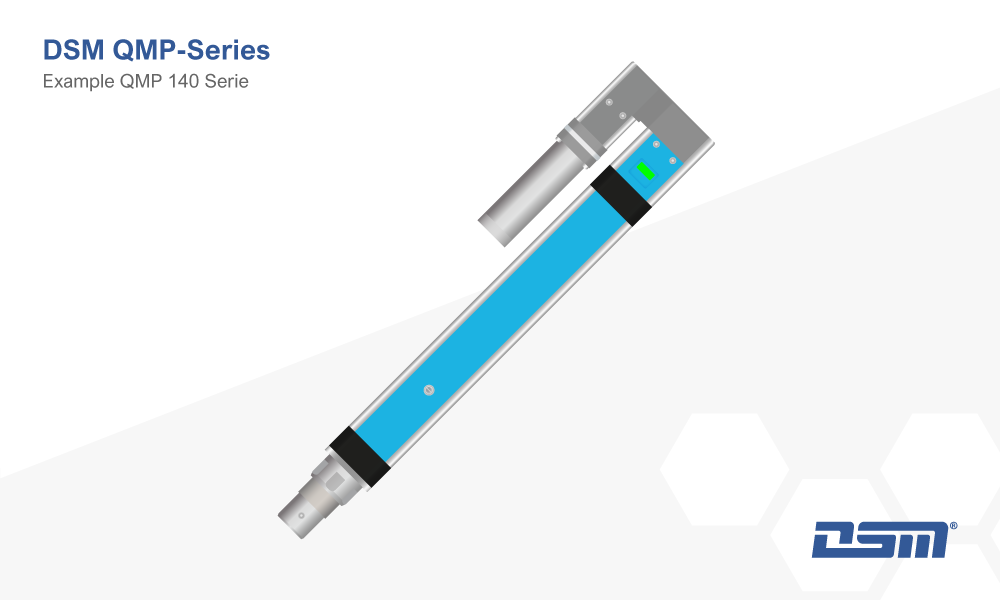
The QMP Series
The DSM QMP Series is characterized by its compact design, integrated force sensor, plunger, absolute stroke measurement system, and built-in LED status indicator.
In combination with the MultiPro 3G control system, it ensures high assembly accuracy and seamless documentation of production data.
The press-in unit is powered by a brushless, electronically controlled servo motor.
Forces
All QMP press-in units are available in compression, tension, or combined compression and tension configurations.
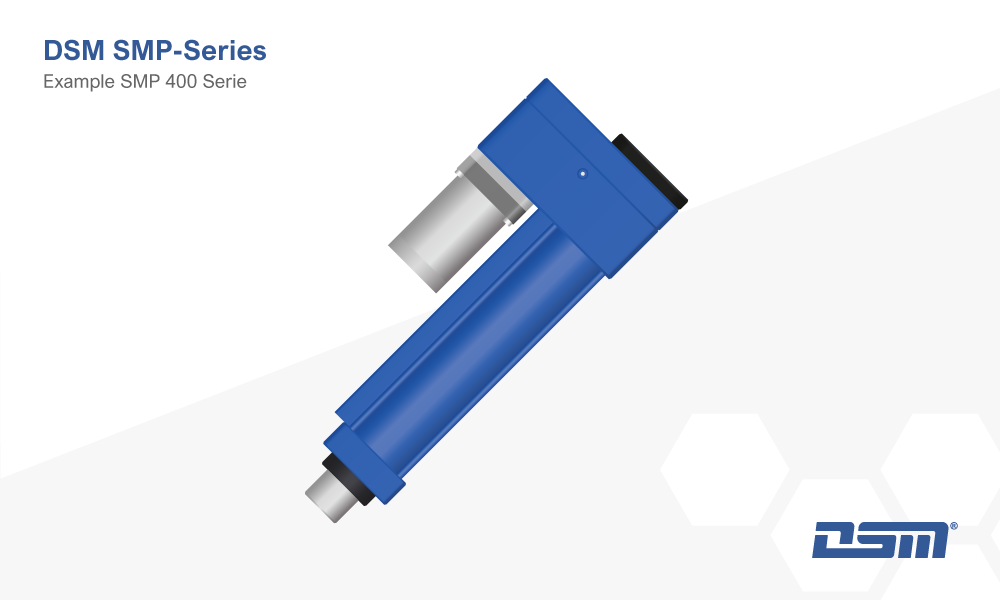
The SMP Series
The DSM SMP Series is characterized by a robust, low-maintenance design, a digital force sensor, and an absolute stroke measurement system.
In combination with the MultiPro 3G control system, it enables high assembly precision and seamless documentation of process data.
Units in this series are powered by a brushless, electronically controlled servo motor mounted at a 90° angle for a more compact integration.
Forces
All SMP press-in units are exclusively designed for compressive forces.